The Biggest Housing Bubble in the World Is in ... Canada?
How real is Canada's housing bubble anyway? More real than any other country's.

(Reuters)
Canada has a new worthwhile initiative. After years of booming prices, that bastion of politeness north of the border is looking to avoid a catastrophic housing bust for something more, well, boring. Initiatives don't get more worthwhile, and perhaps not more difficult considering Canada just might have the biggest housing bubble in the world right now.
Not exactly boring, eh?
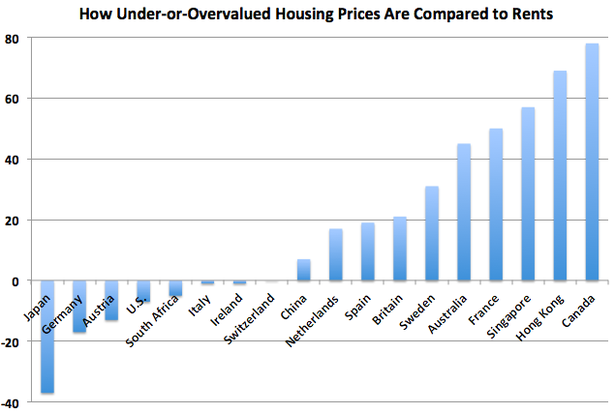
The distinction between higher prices and bubbly prices isn't as subjective as it might sound. Like any other financial asset, there should be a fairly steady relationship between the price of housing and the stream of income -- rent -- it produces. Should be. The chart below, from The Economist, looks at the price-to-rent ratios across different countries, and measures how under-or-overvalued housing is, with negative numbers corresponding to the former and positive ones to the latter.
As realtors like to remind us, every market's different, but there are three big takeaways here.
1) Rich Chinese buyers tend to make for overheated markets. Some of the priciest housing markets in the world have one thing in common, besides low-interest rates (which prevail most everywhere): Chinese expats. Vancouver, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Sydney are among the most popular destinations for wealthy Chinese looking to hedge their bets, and this exit-strategy buying has helped push prices in these locales into the stratosphere.
2) Housing busts can take awhile. After a decade of boom and bust, prices are back to fair value, below it actually, in the U.S. and Ireland, but still have a way to come down in Spain and Britain. Zombie banks tend to be reluctant to realize losses on bad loans, propping up prices in the process, but eventually reality has its day. The sooner that happens, the sooner housing, and construction, can come back.
3) Housing recoveries can take even longer. It was just 20 years ago that the land below the Imperial Palace in Tokyo was supposed to be worth more than all of the land in California combined. But beware the enduring costs of bad macro policy. Too tight money for too long has kept housing prices in hibernation decades on.
Canada is quietly trying to deflate its bubble without any eye-catching headlines. And that means keeping interest rates low while making mortgages harder to get. Now, raising rates to pop a bubble sounds like the kind of hard-hearted long view central bankers pride themselves on, but it's more hard-headed. Higher rates don't just make housing (or any other asset bought with borrowed money) less affordable for new buyers; they make them less affordable for old buyers with adjustable-rate loans too. That sends prices spiraling down and savings racing up, as heavily indebted households, which Canada has no shortage of, try to rebuild their net worths. Higher desired savings outpaces desired investment -- in other words, the economy collapses -- and subsequently cutting rates, even to zero, won't do much to reverse this, as houses and businesses are mostly indifferent to lower borrowing costs while they focus on paying down existing debts. It's what economist Richard Koo calls a "balance sheet recession," and it's a good description of how an economy can get stuck in a liquidity trap.
But by keeping rates where they are and slowly tightening mortgage requirements, Canada hopes to engineer a more gradual price decline that won't set off a vicious circle. In the best case, prices wouldn't fall, except below the rate of inflation, so that real prices decline without hitting household net worths. This strategy is hardly unique -- China has done the same the past few years -- but it has the very Canadian name of "macroprudential regulation".
It's the future of fighting bubbles (which Scott Sumner thinks will only become more common). Let's hope it works. Otherwise, it might turn out that everything went wrong after Canada's housing bubble came along.
Matthew O'Brien is a former senior associate editor at The Atlantic.